GENERAL
The entire Layers interface exists in 3D space. The properties of this 3D space are controlled from the Camera menu and determine how Layers are processed in the final output.
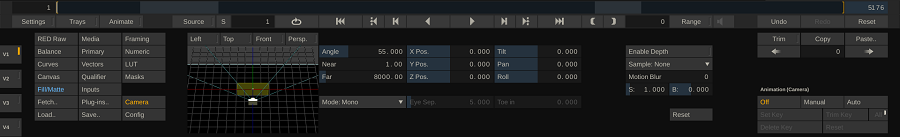
The left section of the Camera menu displays a 3D schematic view of the scene - the relative positions of the camera, Layer and back plane. You can rotate the schematic model in 3D by clicking and dragging it. Alternatively you can use one of the buttons to display the composite in the Viewport from different angles: Left, Top, Front and Perspective. The Perspective view was already discussed in Chapter 5 -The Player and allows you to rotate the schematic scene in the Viewport.
CAMERA CONTROLS
ANGLE
The width of the camera’s viewing range. A wider viewing angle means more distortion as images move to the edges of the frame. A narrower viewing angle decreases the distortion of images near the edge. Since the base image must always fit within the camera angle, changing the angle is the equivalent, in actual camera terms, of a dolly out while zooming in.
NEAR
Distance to the near clipping plane of the camera’s field of view. Any object closer than this will be clipped from the scene.
FAR
Distance to the far clipping plane of the camera’s field of view. Any object further than this will be clipped from the scene.
X, Y, Z POSITION
Determine the camera position in the Scene.
TILT, PAN AND ROLL
Set the Camera's angle position and rotation.
ENABLE DEPTH
When activated, each Layer is layered based on its distance from the camera. This allows Layers to interact within the 3D space. When deactivated, Layers are layered based on their order in the Layers List and their distance from the camera is ignored for the purposes of prioritizing the layering.
SAMPLING
Increasing the number of multi-sampling for smoother animations with performance as a trade of.
MOTION BLUR
The main motion blur control set's the number of temporal samples to use for animations. In addition the S (scale) and B (bias) buttons control the extend of the blur over time and before or after the current frame.
RESET
Reset all controls to their default values.
STEREO SETUP
For Stereo setups you can define two camera's in the 3D scene and set the relative position (Eye Separation) and angle (Toe In) between them. On each Stereo node, with both the left and right eye image as input, you create a single set of Layers. SCRATCH will then use the left camera to render those Layers on the left eye back plane and use the right camera to render the same Layers (but under a different angle) on the right eye back plane. Note that the Stereo camera is only visible in the schematic scene tool when an actual stereo node is selected.